1. 序言
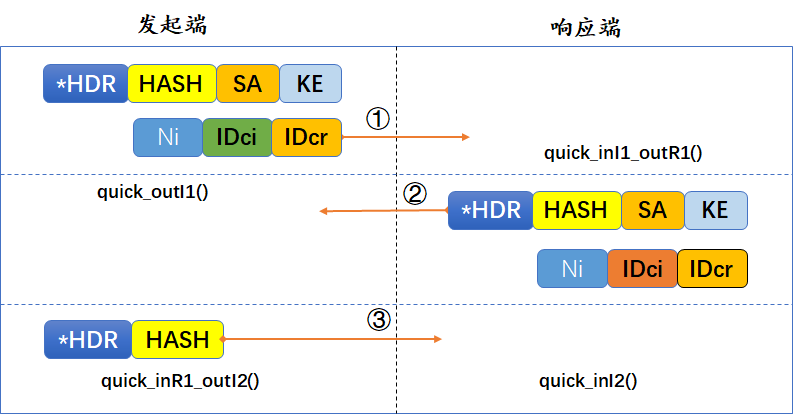
快速模式有三个报文交换,四个核心函数入口。我们已经对前三个函数处理流程对了一个简单的学习和这里,下面对第四个函数入口quick_inI2()的处理流程做一个简单的介绍。
首先需要说明的是快速模式的前两个报文是为了协商感兴趣流的相关参数(如使用的加密算法、认证算法、封装方式、感兴趣流以及生成相关的密钥信息等),而第三个报文则简单了很多:只是为了对前两个报文做认证。那么自然而然引出一个问题:为什么需要第三个报文呢?前两个报文不是已经包含HASH杂凑载荷吗? 供大家思考吧。
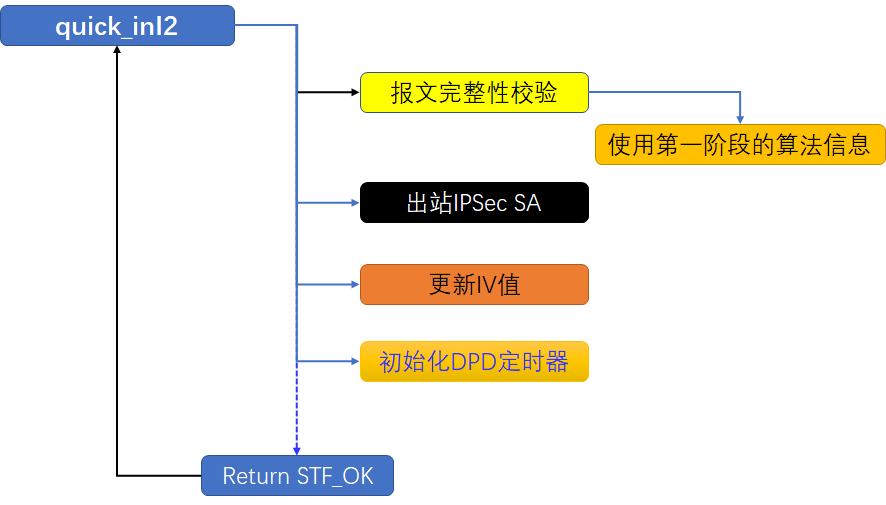
2. quick_inI2()处理流程图
quick_inI2()的处理流程很简单,其中最主要的便是建立出站IPsecSA。(如果IPsec处理流程都是这种精简的,该多好呀:) :) )
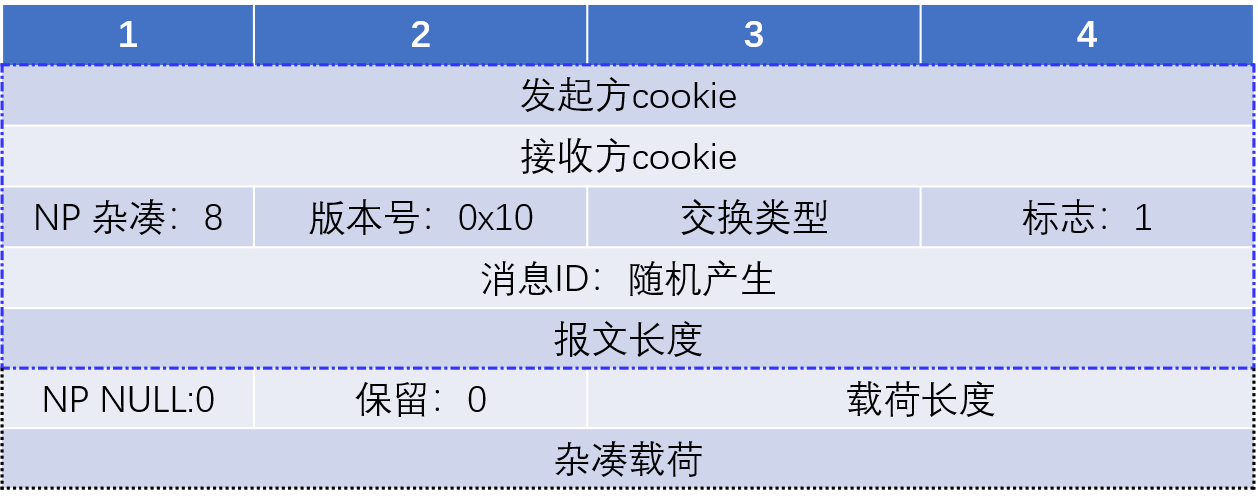
3. 报文格式
quick_inR1_outI2()和quick_inI2()都是用来处理快速模式最后一个包的,报文格式完全一致。,quick_inR1_outI2()包括发送处理流程,而quick_inI2()则只为处理接收流程。
4. quick_inI2()源码
这个源码主要流程很清晰(除了建立IPsecSA),代码也很少。
1 | /* Handle last message of Quick Mode. |
4. 其他接口说明
4.1 hash载荷计算方式
快速模式虽然仅有三个报文交互,但是它们的hash杂凑载荷的计算方式却不相同:
- 第①包计算方式:
$$
HASH(1) = PRF(SKEYID-a, MsgID | SA | Ni | [| IDi | IDr ])
$$ - 第②包计算方式:
$$
HASH(2) = PRF(SKEYID-a, MsgID | Ni | SA | Nr | [| IDi | IDr ])
$$ - 第③包计算方式:
$$
HASH(3) = PRF(SKEYID-a, 0 | MsgID | Ni | Nr)
$$
第①包实现方式和第②包实现方式为同一个函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24/* Compute HASH(1), HASH(2) of Quick Mode.
* HASH(1) is part of Quick I1 message.
* HASH(2) is part of Quick R1 message.
* Used by: quick_outI1, quick_inI1_outR1 (twice), quick_inR1_outI2
* (see RFC 2409 "IKE" 5.5, pg. 18 or draft-ietf-ipsec-ike-01.txt 6.2 pg 25)
*/
size_t
quick_mode_hash12(u_char *dest, const u_char *start, const u_char *roof
, const struct state *st, const msgid_t *msgid, bool hash2)
{
struct hmac_ctx ctx;
hmac_init_chunk(&ctx, st->st_oakley.prf_hasher, st->st_skeyid_a);/*PRF算法 + 认证秘钥*/
hmac_update(&ctx, (const void *) msgid, sizeof(msgid_t));/*填充msgid,由于认证需要msgid,而它唯一*/
if (hash2)
hmac_update_chunk(&ctx, st->st_ni); /* include Ni_b in the hash */
hmac_update(&ctx, start, roof-start);/*数据起始位置和终止位置*/
hmac_final(dest, &ctx);
return ctx.hmac_digest_len;
}第③包实现方式:
1 | /* Compute HASH(3) in Quick Mode (part of Quick I2 message). |
4.2 install_ipsec_sa

5. 小结

IPsec协商流程之主模式+快速模式学习跨度比较久(3个月多),协商流程却是很复杂,而且只是看原理性知识,很多功能都没有敢去涉及,如证书认证、out_sa、 DPD、建立IPsecSA、NAT-T等等。学习期间最主要的体会是:openswan封装了很多很多接口,常用接口需要好好学习,否则在看代码时很困难。就拿out_sa 、out_struct、out_generic等系列,能恶心死人,全文基本都用这几个接口在封装报文和解封装报文,可以说这些基本函数是看openswan源码的接口。
后面计划继续更新几个函数接口实现,也是以前学习整理过程中遗留的坑,先填几个然后在更新学习其他流程。